Calculo Manual Excel Mac
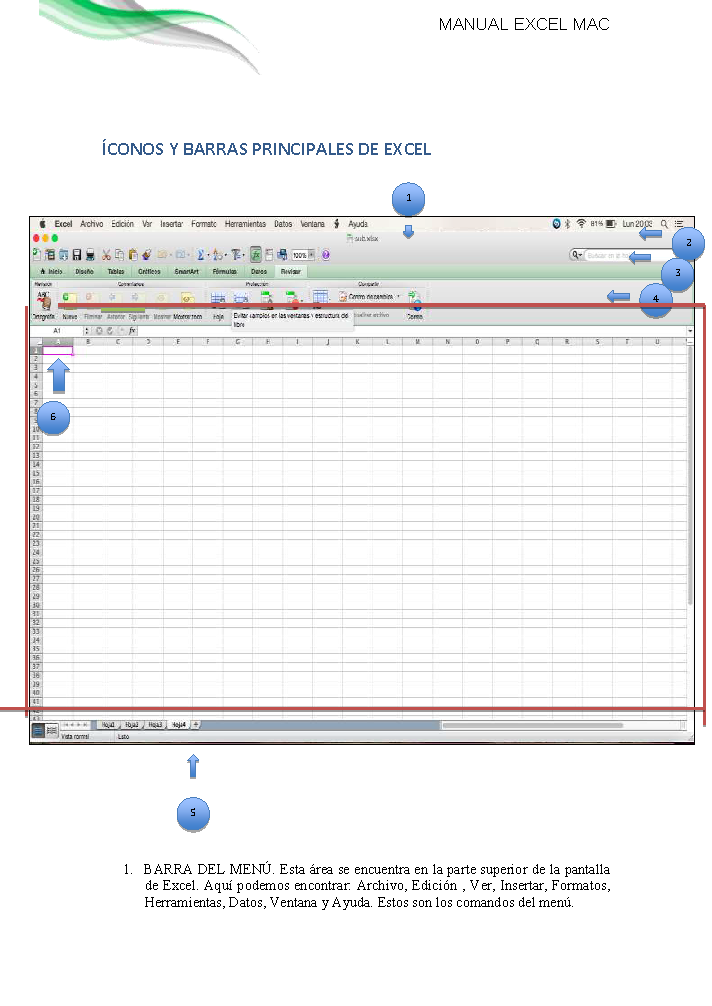
Excel for Office 365 for Mac Excel 2019 for Mac Excel 2016 for Mac More. Looking for something that’s not listed here? Use the Search box in the upper right corner of this window. Office 2016 for Mac Quick Start Guides. Create a drop-down list. Conditional formatting. Save time and conquer the spreadsheet with these 50 Excel keyboard shortcuts. Get the most out of Excel in Windows with these pro tips. This is an accessible template. Download Share. More templates like this. Drop-down tutorial Excel Welcome to Excel Excel 5 ways to keep your work safe and secure. Automatically convert date systems: When selected, Excel automatically corrects for differences between the 1900 (Windows) and 1904 date systems (Mac) during copy and paste. The destination workbook’s format is adopted. AutoCorrect: You can have Excel fix your common typing blunders automatically. To begin, click the “File” tab. On the backstage screen, click “Options” in the list of items on the left. The Excel Options dialog box displays. Click “Formulas” in the list of items on the left. In the Calculation options section, click the “Manual” radio button to turn on the ability to manually calculate each worksheet. For example, if Auto2.xlsx contains three worksheets, changing the mode of calculation of the first worksheet to manual also changes the mode of calculation to manual in the other two sheets. If all other documents are closed and you create a new document, the new document uses the same calculation mode as the previously closed documents.
Se aplica a: Excel Excel 2013 Excel 2016 VBAApplies to: Excel Excel 2013 Excel 2016 VBA
La 'cuadrícula grande' de 1 millón de filas y 16 000 columnas en Office Excel 2016, junto con el aumento de otros muchos límites, aumenta enormemente el tamaño de las hojas de cálculo que puede crear con respecto a versiones anteriores de Excel.The 'Big Grid' of 1 million rows and 16,000 columns in Office Excel 2016, together with many other limit increases, greatly increases the size of worksheets that you can build compared to earlier versions of Excel.Ahora una única hoja de cálculo de Excel puede contener más de 1 000 veces la cantidad de celdas que en versiones anteriores.A single worksheet in Excel can now contain over 1,000 times as many cells as earlier versions.
Manual Excel Romana
En versiones anteriores de Excel, muchas personas creaban hojas de cálculo lentas y las hojas de cálculo más grandes suelen calcular más lentamente que las pequeñas.In earlier versions of Excel, many people created slow-calculating worksheets, and larger worksheets usually calculate more slowly than smaller ones.Con la introducción de la 'Gran cuadrícula' en Excel 2007, el rendimiento importa mucho.With the introduction of the 'Big Grid' in Excel 2007, performance really matters.La lentitud en el cálculo y las tareas de manipulación de datos, como ordenar y filtrar, hace que resulte más difícil para los usuarios concentrarse en la tarea en curso, y la falta de concentración aumenta el número de errores.Slow calculation and data manipulation tasks such as sorting and filtering make it more difficult for users to concentrate on the task at hand, and lack of concentration increases errors.
Las versiones recientes de Excel introdujeron varias características para ayudarle a controlar este aumento de capacidad, como la capacidad de usar más de un procesador a la vez para los cálculos y las operaciones comunes de conjunto de datos, como la apertura, ordenación y actualización de libros.Recent Excel versions introduced several features to help you handle this capacity increase, such as the ability to use more than one processor at a time for calculations and common data set operations like refresh, sorting, and opening workbooks.El cálculo multiproceso puede reducir sustancialmente el tiempo de cálculo de la hoja de cálculo.Multithreaded calculation can substantially reduce worksheet calculation time.Sin embargo, el factor más importantes que influye en la velocidad de cálculo de Excel sigue siendo la forma en que la hoja de cálculo está diseñada y creada.However, the most important factor that influences Excel calculation speed is still the way your worksheet is designed and built.
Puede modificar la mayoría de las hojas de cálculo de cálculo lento para calcular decenas, cientos o incluso miles de veces más rápido.You can modify most slow-calculating worksheets to calculate tens, hundreds, or even thousands of times faster.Al identificar, medir y mejorar los obstáculos de cálculo en las hojas de cálculo, puede acelerar el proceso de cálculo.By identifying, measuring, and then improving the calculation obstructions in your worksheets, you can speed up calculation.
La importancia de la velocidad de cálculoThe importance of calculation speed
La baja velocidad de cálculo afecta a la productividad y aumenta los errores del usuario.Poor calculation speed affects productivity and increases user error.La productividad del usuario y la capacidad de centrarse en una tarea se deteriora a medida que el tiempo de respuesta aumenta.User productivity and the ability to focus on a task deteriorates as response time lengthens.
Excel tiene dos modos de cálculo principales que le permiten controlar cuándo se produce el cálculo:Excel has two main calculation modes that let you control when calculation occurs:
Cálculo automático: las fórmulas se actualizan automáticamente cuando se realiza un cambio.Automatic calculation - Formulas are automatically recalculated when you make a change.
Cálculo manual: las fórmulas se actualizan cuando se solicita (por ejemplo, al presionar F9).Manual calculation - Formulas are recalculated only when you request it (for example, by pressing F9).
En los tiempos de cálculo de menos de una décima de segundo, para los usuarios parece que el sistema está respondiendo al instante.For calculation times of less than about a tenth of a second, users feel that the system is responding instantly.Pueden usar el cálculo automático incluso cuando escriben datos.They can use automatic calculation even when they enter data.
Entre una décima de segundo y un segundo, los usuarios pueden mantener correctamente el flujo de ideas, aunque notarán el retraso en el tiempo de respuesta.Between a tenth of a second and one second, users can successfully keep a train of thought going, although they will notice the response time delay.
A medida que aumenta el tiempo de cálculo (normalmente entre 1 y 10 segundos), los usuarios deben cambiar a cálculo manual cuando escriben datos.As calculation time increases (usually between 1 and 10 seconds), users must switch to manual calculation when they enter data.Los errores del usuario y los niveles de molestia empiezan a aumentar, especialmente en tareas repetitivas, y es difícil mantener la concentración.User errors and annoyance levels start to increase, especially for repetitive tasks, and it becomes difficult to maintain a train of thought.
Para tiempos de cálculo mayores de 10 segundos, los usuarios pasan a estar impacientes y normalmente pasan a otras tareas mientras esperan.For calculation times greater than 10 seconds, users become impatient and usually switch to other tasks while they wait.Esto puede provocar problemas cuando el cálculo es parte de una secuencia de tareas y el usuario pierde el hilo.This can cause problems when the calculation is one of a sequence of tasks and the user loses track.
Información sobre los métodos de cálculo de ExcelUnderstanding calculation methods in Excel
Para mejorar el rendimiento de cálculo en Excel, debe comprender los métodos de cálculo disponibles y cómo controlarlos.To improve the calculation performance in Excel, you must understand both the available calculation methods and how to control them.
Cálculo completo y dependencias de actualizaciónFull calculation and recalculation dependencies
El motor inteligente de recálculo en Excel intenta minimizar el tiempo de cálculo mediante el seguimiento continuo de precedentes y dependencias de cada fórmula (las celdas a las que hace referencia la fórmula) y los cambios realizados desde el último cálculo.The smart recalculation engine in Excel tries to minimize calculation time by continuously tracking both the precedents and dependencies for each formula (the cells referenced by the formula) and any changes that were made since the last calculation.En la próxima actualización del cálculo, Excel solo vuelve a calcular lo siguiente:At the next recalculation, Excel recalculates only the following:
Celdas, fórmulas, valores o nombres que han cambiado o se han marcado porque necesiten actualizarse.Cells, formulas, values, or names that have changed or are flagged as needing recalculation.
Celdas dependientes de otras celdas, fórmulas, nombres o valores que necesitan actualizarse.Cells dependent on other cells, formulas, names, or values that need recalculation.
Funciones variables y los formatos condicionales visibles.Volatile functions and visible conditional formats.
Excel sigue calculando celdas que dependen de celdas calculadas anteriormente, incluso si el valor de la celda calculada anteriormente no cambia cuando se calcula.Excel continues calculating cells that depend on previously calculated cells even if the value of the previously calculated cell does not change when it is calculated.
Puesto que en la mayoría de los casos solo cambia una parte de los datos de entrada o unas pocas fórmulas entre cálculos, esta actualización inteligente normalmente tarda solo una fracción del tiempo que se tardaría un cálculo completo de todas las fórmulas.Because you change only part of the input data or a few formulas between calculations in most cases, this smart recalculation usually takes only a fraction of the time that a full calculation of all the formulas would take.
En el modo de cálculo manual, puede activar esta actualización inteligente presionando F9.In manual calculation mode, you can trigger this smart recalculation by pressing F9.Puede forzar un cálculo completo de todas las fórmulas presionando Ctrl+Alt+F9 o puede forzar una reconstrucción completa de las dependencias y un cálculo completo presionando Mayús+Ctrl+Alt+F9.You can force a full calculation of all the formulas by pressing Ctrl+Alt+F9, or you can force a complete rebuild of the dependencies and a full calculation by pressing Shift+Ctrl+Alt+F9.
Proceso de cálculoCalculation process
Las fórmulas de Excel que hacen referencia a otras celdas se pueden poner antes o después de las celdas de referencia (referencia hacia delante o referencia hacia atrás).Excel formulas that reference other cells can be put before or after the referenced cells (forward referencing or backward referencing).Esto es porque Excel no calcula las celdas en un orden fijo ni por fila o columna.This is because Excel does not calculate cells in a fixed order, or by row or column.En su lugar, Excel determina dinámicamente la secuencia de cálculo en función de una lista de todas las fórmulas para calcular (la cadena de cálculo) y la información de dependencia sobre cada fórmula.Instead, Excel dynamically determines the calculation sequence based on a list of all the formulas to calculate (the calculation chain) and the dependency information about each formula.
Excel tiene fases de cálculo diferentes:Excel has distinct calculation phases:
Crear la cadena inicial de cálculo y determinar dónde empezar a calcular.Build the initial calculation chain and determine where to begin calculating.Esta fase se produce cuando el libro se carga en la memoria.This phase occurs when the workbook is loaded into memory.
Seguir las dependencias, marcar las celdas sin calcular y actualizar la cadena de cálculo.Track dependencies, flag cells as uncalculated, and update the calculation chain.Esta fase se ejecuta en cada entrada o cambio de celda, incluso en el modo de cálculo manual.This phase executes at each cell entry or change, even in manual calculation mode.Normalmente, este paso se ejecuta tan rápido que no lo nota, pero en casos complejos, pueden tardar en responder.Ordinarily this executes so fast that you do not notice it, but in complex cases, response can be slow.
Calcular todas las fórmulas.Calculate all formulas.Como parte del proceso de cálculo, Excel reordena y reestructura la cadena de cálculo para optimizar futuros cálculos.As a part of the calculation process, Excel reorders and restructures the calculation chain to optimize future recalculations.
Actualizar las partes visibles de la ventana de Excel.Update the visible parts of the Excel windows.
La tercera fase se ejecuta en cada cálculo o actualización.The third phase executes at each calculation or recalculation.Excel intenta calcular cada fórmula en la cadena de cálculo una a una, pero si una fórmula depende de una o varias fórmulas que aún no se han calculado, la fórmula se envía hacia el final de la cadena para calcularse de nuevo más tarde.Excel tries to calculate each formula in the calculation chain in turn, but if a formula depends on one or more formulas that have not yet been calculated, the formula is sent down the chain to be calculated again later.Esto significa que una fórmula se puede calcular varias veces en cada actualización.This means that a formula can be calculated multiple times per recalculation.
La segunda vez que se calcula un libro suele ser considerablemente más rápida que la primera vez.The second time that you calculate a workbook is often significantly faster than the first time.Esto ocurre por varias razones:This occurs for several reasons:
Normalmente, Excel actualiza solo las celdas que han cambiado y sus celdas dependientes.Excel usually recalculates only cells that have changed, and their dependents.
Excel almacena y vuelve a usar la secuencia de cálculo más reciente para que pueda omitir la mayor parte del tiempo que se utiliza para determinar el orden de cálculo.Excel stores and reuses the most recent calculation sequence so that it can save most of the time used to determine the calculation sequence.
En equipos de varios núcleos, Excel intenta optimizar la forma en que los cálculos están distribuidos entre los núcleos según los resultados del cálculo anterior.With multiple core computers, Excel tries to optimize the way the calculations are spread across the cores based on the results of the previous calculation.
En una sesión de Excel, tanto Windows como Excel almacenan en caché programas y datos usados recientemente para acelerar el acceso.In an Excel session, both Windows and Excel cache recently used data and programs for faster access.
Calcular libros, hojas de cálculo y rangosCalculating workbooks, worksheets, and ranges
Puede controlar lo que se calcula mediante los diferentes métodos de cálculo de Excel.You can control what is calculated by using the different Excel calculation methods.
Calcular todos los libros abiertosCalculate all open workbooks
Cada actualización y cálculo completo calcula todos los libros abiertos actualmente, resuelve las dependencias dentro de cada libro y entre libros y hojas de cálculo y restablece todas las celdas sin calcular anteriormente (incorrectas) como calculadas.Each recalculation and full calculation calculates all the workbooks that are currently open, resolves any dependencies within and between workbooks and worksheets, and resets all previously uncalculated (dirty) cells as calculated.
Calcular las hojas seleccionadasCalculate selected worksheets
También puede actualizar sólo las hojas seleccionadas usando Mayús+F9.You can also recalculate only the selected worksheets by using Shift+F9.Esto no resolverá ninguna dependencia entre hojas de cálculo y no restablecerá las celdas incorrectas como calculadas.This does not resolve any dependencies between worksheets, and does not reset dirty cells as calculated.
Un rango de celdasCalculate a range of cells
Excel también permite el cálculo de un rango de celdas usando los métodos Range.CalculateRowMajorOrder y Range.Calculate de Visual Basic para Aplicaciones (VBA):Excel also allows for the calculation of a range of cells by using the Visual Basic for Applications (VBA) methods Range.CalculateRowMajorOrder and Range.Calculate:
Range.CalculateRowMajorOrder calcula el rango de izquierda a derecha y de arriba a abajo, ignorando todas las dependencias.Range.CalculateRowMajorOrder calculates the range left to right and top to bottom, ignoring all dependencies.
Range.Calculate calcula el rango resolviendo todas las dependencias del rango.Range.Calculate calculates the range resolving all dependencies within the range.
Puesto que CalculateRowMajorOrder no soluciona dependencias dentro del rango que se calcula, suele ser considerablemente más rápido que Range.Calculate.Because CalculateRowMajorOrder does not resolve any dependencies within the range that is being calculated, it is usually significantly faster than Range.Calculate.Sin embargo, debería usarse con cuidado porque puede no devolver los mismos resultados que Range.Calculate.However, it should be used with care because it may not give the same results as Range.Calculate.
Range.Calculate es una de las herramientas más útiles en Excel para optimizar el rendimiento, ya que puede usarse para medir el tiempo y comparar la velocidad de distintas fórmulas de cálculo.Range.Calculate is one of the most useful tools in Excel for performance optimization because you can use it to time and compare the calculation speed of different formulas.
Para obtener más información, vea Rendimiento de Excel: mejoras de rendimiento y límites.For more information, see Excel performance: Performance and limit improvements.
Funciones volátilesVolatile functions
Una función volátil siempre se recalcula en cada actualización, aunque no parezca tener ningún precedentes cambiado.A volatile function is always recalculated at each recalculation even if it does not seem to have any changed precedents.El uso de muchas funciones variables ralentiza cada actualización, pero afecta en un cálculo completo.Using many volatile functions slows down each recalculation, but it makes no difference to a full calculation.Puede hacer una función definida por el usuario volátil incluyendo Application.Volatile en el código de la función.You can make a user-defined function volatile by including Application.Volatile in the function code.
Algunas de las funciones integradas de Excel son obviamente volátiles: RAND(), NOW(), TODAY().Some of the built-in functions in Excel are obviously volatile: RAND(), NOW(), TODAY().En otras es menos evidente: OFFSET(), CELL(), INDIRECT(), INFO().Others are less obviously volatile: OFFSET(), CELL(), INDIRECT(), INFO().
Algunas funciones que anteriormente se han documentado como volátiles en realidad no lo son: INDEX(), ROWS(), COLUMNS(), AREAS().Some functions that have previously been documented as volatile are not in fact volatile: INDEX(), ROWS(), COLUMNS(), AREAS().
Acciones volátilesVolatile actions
Las acciones volátiles son acciones que desencadenan un nuevo cálculo e incluyen las siguientes:Volatile actions are actions that trigger a recalculation, and include the following:
- Hacer clic en un divisor de fila o columna en modo automático.Clicking a row or column divider when in automatic mode.
- Insertar o eliminar filas, columnas o celdas en una hoja.Inserting or deleting rows, columns, or cells on a sheet.
- Agregar, cambiar o eliminar nombres definidos.Adding, changing, or deleting defined names.
- Cambiar el nombre o la posición de la hoja de cálculo en el modo automático.Renaming worksheets or changing worksheet position when in automatic mode.
- Filtrar, ocultar o mostrar filas.Filtering, hiding, or un-hiding rows.
- Abrir un libro en modo automático.Opening a workbook when in automatic mode.Si el libro se ha calculado por última vez en una versión diferente de Excel, abrir el libro normalmente ocasiona un cálculo completo.If the workbook was last calculated by a different version of Excel, opening the workbook usually results in a full calculation.
- Guardar un libro en modo manual si la opción Calcular antes de guardar está seleccionada.Saving a workbook in manual mode if the Calculate before Save option is selected.
Circunstancias de evaluación de fórmulas y nombresFormula and name evaluation circumstances
Una fórmula o parte de una fórmula se evalúa (calcula) inmediatamente, incluso en el modo de cálculo manual, al realizar uno de estos procedimientos:A formula or part of a formula is immediately evaluated (calculated), even in manual calculation mode, when you do one of the following:
- Escribir o editar la fórmula.Enter or edit the formula.
- Escribir o editar la fórmula con el Asistente de funciones.Enter or edit the formula by using the Function Wizard.
- Escribir la fórmula como argumento en el Asistente de funciones.Enter the formula as an argument in the Function Wizard.
- Seleccionar la fórmula en la barra de fórmulas y presionar F9 (presione Esc para deshacer y revertir la fórmula) o hacer clic en Evaluar fórmula.Select the formula in the formula bar and press F9 (press Esc to undo and revert to the formula), or click Evaluate Formula.
Una fórmula se marca como no calculada cuando hace referencia a (depende de) una celda o fórmula que tiene una de estas condiciones:A formula is flagged as uncalculated when it refers to (depends on) a cell or formula that has one of these conditions:
- Se ha insertado.It was entered.
- Se ha cambiado.It was changed.
- Está en una lista de Autofiltro y se ha habilitado la lista desplegable de criterios.It is in an AutoFilter list, and the criteria drop-down list was enabled.
- Se ha marcado como no calculada.It is flagged as uncalculated.
Una fórmula que está marcada como no calculada se evalúa cuando se calcula o se vuelve a calcular la hoja de cálculo, libro o instancia de Excel que la contiene.A formula that is flagged as uncalculated is evaluated when the worksheet, workbook, or Excel instance that contains it is calculated or recalculated.
Las condiciones que hacen que un nombre definido se evalúe son distintas que para una fórmula en una celda:The circumstances that cause a defined name to be evaluated differ from those for a formula in a cell:
- Un nombre definido se evalúa cada vez que se evalúa una fórmula que le hace referencia, por lo que usar un nombre en varias fórmulas puede hacer que el nombre se evalúe varias veces.A defined name is evaluated every time that a formula that refers to it is evaluated so that using a name in multiple formulas can cause the name to be evaluated multiple times.
- Los nombres a los que no hace referencia ninguna fórmula no se calculan, ni siquiera en un cálculo completo.Names that are not referred to by any formula are not calculated even by a full calculation.
Tablas de datosData tables
Las tablas de datos de Excel (ficha Datos > grupo Herramientas de datos > Análisis de hipótesis > Tabla de datos) no deben confundirse con la característica de tabla (pestaña Inicio > grupo Estilos > Dar formato como tabla, o bien, pestaña Insertar > grupo ** Tablas** > Tabla).Excel data tables (Data tab > Data Tools group > What-If Analysis > Data Table) should not be confused with the table feature (Home tab > Styles group > Format as Table, or, Insert tab > Tables group > Table).Las tablas de datos de Excel realizan varios cálculos del libro, cada uno impulsado por los diferentes valores de la tabla.Excel data tables do multiple recalculations of the workbook, each driven by the different values in the table.Excel calcula primero el libro normalmente.Excel first calculates the workbook normally.Después, para cada par de valores de fila y columna, sustituye los valores, hace un nuevo cálculo de subproceso único y almacena los resultados en la tabla de datos.For each pair of row and column values, it then substitutes the values, does a single-threaded recalculation, and stores the results in the data table.
La actualización de tabla de datos siempre usa un solo procesador.Data table recalculation always uses only a single processor.
Las tablas de datos ofrecen una forma cómoda para calcular varias variaciones y ver y comparar los resultados de las variaciones.Data tables give you a convenient way to calculate multiple variations and view and compare the results of the variations.Use la opción de cálculo Automático excepto en tablas para evitar que Excel desencadene automáticamente los múltiples cálculos en cada cálculo mientras sigue calculando todas las fórmulas dependientes, a excepción de las tablas.Use the Automatic except Tables calculation option to stop Excel from automatically triggering the multiple calculations at each calculation, but still calculate all dependent formulas except tables.
Control de las opciones de cálculoControlling calculation options
Excel tiene una serie de opciones que le permiten controlar la forma en que calcula.Excel has a range of options that enable you to control the way it calculates.Puede cambiar las opciones más usadas en Excel usando el grupo Cálculo en la pestaña Fórmulas en la cinta de opciones.You can change the most frequently used options in Excel by using the Calculation group on the Formulas tab on the Ribbon.
Figura 1. Grupo de cálculo en la ficha FórmulasFigure 1. Calculation group on the Formulas tab
Para ver más opciones de cálculo de Excel, en la ficha Archivo, haga clic en Opciones.To see more Excel calculation options, on the File tab, click Options.En el cuadro de diálogo Opciones de Excel, haga clic en la ficha Fórmulas.In the Excel Options dialog box, click the Formulas tab.
Figura 2. Opciones de cálculo en la ficha Fórmulas en Opciones de ExcelFigure 2. Calculation options on the Formulas tab in Excel Options
Muchas opciones de cálculo (Automático, Automático excepto para tablas de datos, Manual, Volver a calcular libro antes de guardarlo) y la configuración de la iteración (Habilitar cálculo iterativo, Iteraciones máximas, Cambio máximo) funcionan en el nivel de aplicación en lugar de en el nivel de libro (son las mismas para todos los libros abiertos).Many calculation options (Automatic, Automatic except for data tables, Manual, Recalculate workbook before saving) and the iteration settings (Enable iterative calculation, Maximum Iterations, Maximum Change) operate at the application level instead of at the workbook level (they are the same for all open workbooks).
Para ver las opciones de cálculo avanzadas de Excel, en la ficha Archivo, haga clic en Opciones.To find advanced calculation options, on the File tab, click Options.En el cuadro de diálogo Opciones de Excel, haga clic en **Avanzadas **.In the Excel Options dialog box, click Advanced.En la sección Fórmulas establezca las opciones de cálculo.Under the Formulas section, set calculation options.
Figura 3. Opciones de cálculo avanzadasFigure 3. Advanced calculation options
Cuando inicia Excel o cuando se está ejecutando sin libros abiertos, el modo de cálculo inicial y las opciones de iteración se establecen a partir del primer libro que no sea plantilla ni complemento que abra.When you start Excel, or when it is running without any workbooks open, the initial calculation mode and iteration settings are set from the first non-template, non-add-in workbook that you open.Esto significa que la configuración del cálculo en libros abiertos más adelante se ignora, aunque, por supuesto, puede cambiar manualmente la configuración de Excel en cualquier momento.This means that the calculation settings in workbooks opened later are ignored, although, of course, you can manually change the settings in Excel at any time.Al guardar un libro, la configuración de cálculo actual se almacena en el libro.When you save a workbook, the current calculation settings are stored in the workbook.
Cálculo automáticoAutomatic calculation
El modo de cálculo automático significa que Excel actualiza automáticamente todos los libros abiertos en todos los cambios y al abrir un libro.Automatic calculation mode means that Excel automatically recalculates all open workbooks at every change and when you open a workbook.Normalmente, cuando abre un libro en el modo automático y Excel lo actualiza, no verá el nuevo cálculo porque nada ha cambiado desde que se guardó el libro.Usually when you open a workbook in automatic mode and Excel recalculates, you do not see the recalculation because nothing has changed since the workbook was saved.
Puede que note este cálculo al abrir un libro en una versión de Excel posterior a la que usó la última vez que se calculó el libro (por ejemplo, Excel 2016 y Excel 2013).You might notice this calculation when you open a workbook in a later version of Excel than you used the last time that the workbook was calculated (for example, Excel 2016 versus Excel 2013).Puesto que los motores de cálculo de Excel son diferentes, Excel realiza un cálculo completo cuando se abre un libro que se guardó con una versión anterior de Excel.Because the Excel calculation engines are different, Excel performs a full calculation when it opens a workbook that was saved using an earlier version of Excel.
Cálculo manualManual calculation
El modo de cálculo manual significa que Excel actualiza todos los libros abiertos solo cuando se solicita presionando F9 o Ctrl+Alt+F9, o cuando guarda un libro.Manual calculation mode means that Excel recalculates all open workbooks only when you request it by pressing F9 or Ctrl+Alt+F9, or when you save a workbook.Para los libros que tardan más de una fracción de un segundo en actualizarse, debe establecer el cálculo en modo manual para evitar un retraso al realizar cambios.For workbooks that take more than a fraction of a second to recalculate, you must set calculation to manual mode to avoid a delay when you make changes.
Excel le indica cuando un libro en el modo manual necesita actualizarse mostrando Calcular en la barra de estado.Excel tells you when a workbook in manual mode needs recalculation by displaying Calculate in the status bar.Esta barra de estado también muestra Calcular si el libro contiene referencias circulares y se selecciona la opción de iteración.The status bar also displays Calculate if your workbook contains circular references and the iteration option is selected.
Configuración de iteraciónIteration settings
Si tiene referencias circulares intencionadas en el libro, la configuración de iteración le permite controlar el número máximo de veces que el libro se actualiza (iteraciones) y los criterios de convergencia (cambio máximo: cuándo parar).If you have intentional circular references in your workbook, the iteration settings enable you to control the maximum number of times the workbook is recalculated (iterations) and the convergence criteria (maximum change: when to stop).Desactive la casilla de iteración para que, si tiene referencias circulares accidentales, Excel le advierta y no intente resolverlos.Clear the iteration box so that if you have accidental circular references, Excel will warn you and will not try to solve them.
Propiedad de libro ForceFullCalculationWorkbook ForceFullCalculation property
Al establecer esta propiedad de libro como True, la actualización inteligente de Excel se desactiva y cada vez que se vuelve a calcular se calculan todas las fórmulas de todos los libros abiertos.When you set this workbook property to True, Excel's Smart Recalculation is turned off and every recalculation recalculates all the formulas in all the open workbooks.Para algunos libros complejos, el tiempo necesario para crear y mantener los árboles de dependencia necesarios para la actualización inteligente es mayor que el tiempo ahorrado con ella.For some complex workbooks, the time taken to build and maintain the dependency trees needed for Smart Recalculation is larger than the time saved by Smart Recalculation.
Si el libro tarda demasiado tiempo en abrirse o si realizar cambios pequeños toma mucho tiempo incluso en el modo de cálculo manual, puede ser preferible intentar usar ForceFullCalculation.If your workbook takes an excessively long time to open, or making small changes takes a long time even in manual calculation mode, it may be worth trying ForceFullCalculation.
Calcular aparecerá en la barra de estado si la propiedad ForceFullCalculation del libro se ha establecido en True.Calculate will appear in the status bar if the workbook ForceFullCalculation property has been set to True.
Puede controlar esta configuración con el VBE (ALT+F11), seleccionando ThisWorkbook en el Explorador de proyectos (Ctrl+R) y mostrando la Ventana Propiedades (F4).You can control this setting using the VBE (Alt+F11), selecting ThisWorkbook in the Project Explorer (Ctrl+R) and showing the Properties Window (F4).
Figura 4. Establecer la propiedad Workbook.ForceFullCalculationFigure 4. Setting the Workbook.ForceFullCalculation property
Hacer que los libros calculen más rápidoMaking workbooks calculate faster
Use los siguientes métodos y pasos para hacer que los libros calculen más rápido.Use the following steps and methods to make your workbooks calculate faster.
Velocidad del procesador y varios núcleosProcessor speed and multiple cores
En la mayoría de las versiones de Excel, un procesador más rápido, por supuesto, permitirá un cálculo de Excel más rápido.For most versions of Excel, a faster processor will, of course, enable faster Excel calculation.El motor de cálculo multiproceso introducido en Excel 2007 permite a Excel aprovechar los sistemas con varios procesadores y puede esperar mejoras de rendimiento importantes con la mayoría de libros.The multithreaded calculation engine introduced in Excel 2007 enables Excel to make excellent use of multiprocessor systems, and you can expect significant performance gains with most workbooks.
Para la mayoría de los libros grandes, la mejora en el rendimiento de cálculo aumenta de forma casi lineal con el número de procesadores físicos.For most large workbooks, the calculation performance gains from multiple processors scale almost linearly with the number of physical processors.Sin embargo, el 'hyper-threading' de procesadores físicos solo genera una pequeña ganancia de rendimiento.However, hyper-threading of physical processors only produces a small performance gain.
Para obtener más información, vea Rendimiento de Excel: mejoras de rendimiento y límites.For more information, see Excel performance: Performance and limit improvements.
RAMRAM
La paginación a un archivo de paginación de memoria virtual es lenta.Paging to a virtual-memory paging file is slow.Debe tener suficiente RAM física para los libros, Excel y el sistema operativo.You must have enough physical RAM for the operating system, Excel, and your workbooks.Si suele tener actividad en el disco duro durante el cálculo y no está usando funciones definidas por el usuario que activen la actividad del disco, necesita más memoria RAM.If you have more than occasional hard disk activity during calculation, and you are not running user-defined functions that trigger disk activity, you need more RAM.
Como se ha mencionado, las versiones recientes de Excel pueden realizar un uso eficaz de grandes cantidades de memoria y la versión de 32 bits de Excel 2007 y Excel 2010 puede controlar un único libro o una combinación de libros con un máximo de 2 GB de memoria.As mentioned, recent versions of Excel can make effective use of large amounts of memory, and the 32-bit version of Excel 2007 and Excel 2010 can handle a single workbook or a combination of workbooks using up to 2 GB of memory.
Las versiones de 32 bits de Excel 2013 y Excel 2016 que usan la función Large Address Aware (LAA) pueden usar un máximo de 3 o 4 GB de memoria, dependiendo de la versión de Windows instalada.The 32-bit versions of Excel 2013 and Excel 2016 that use the Large Address Aware (LAA) feature can use up to 3 or 4 GB of memory, depending on the version of Windows installed.La versión de 64 bits de Excel puede controlar libros más grandes.The 64-bit version of Excel can handle larger workbooks.Para obtener más información, vea la sección 'Grandes conjuntos de datos, LAA y Excel de 64 bits' en rendimiento de Excel: mejoras de rendimiento y límite.For more information, see the 'Large data sets, LAA, and 64-bit Excel' section in Excel performance: Performance and limit improvements.
Una directriz aproximada para el cálculo eficaz es tener suficiente RAM para el conjunto más grande de libros que necesita tener abiertos al mismo tiempo, más entre 1 y 2 GB para Excel y el sistema operativo, más RAM adicional para otras aplicaciones en ejecución.A rough guideline for efficient calculation is to have enough RAM to hold the largest set of workbooks that you need to have open at the same time, plus 1 to 2 GB for Excel and the operating system, plus additional RAM for any other running applications.
Medir el tiempo de cálculoMeasuring calculation time
Para que los libros calculen más rápido, debe ser capaz de medir con precisión el tiempo de cálculo.To make workbooks calculate faster, you must be able to accurately measure calculation time.Necesita un temporizador que sea más rápido y preciso que la función Time de VBA.You need a timer that is faster and more accurate than the VBA Time function.La función MICROTIMER() que se muestra en el ejemplo siguiente usa llamadas API de Windows al temporizador de alta resolución del sistema.The MICROTIMER() function shown in the following code example uses Windows API calls to the system high-resolution timer.Pueden medir intervalos de tiempo de un pequeño número de microsegundos.It can measure time intervals down to small numbers of microseconds.Tenga en cuenta que como Windows es un sistema operativo multitarea y la segunda vez que se calcula un elemento será más rápido que la primera vez, el tiempo obtenido normalmente no se repetirá exactamente.Be aware that because Windows is a multitasking operating system, and because the second time that you calculate something, it may be faster than the first time, the times that you get usually do not repeat exactly.Para lograr la mejor precisión, mida las tareas de cálculo varias veces y calcule el promedio de los resultados.To achieve the best accuracy, measure time calculation tasks several times and average the results.
Para obtener más información sobre cómo el Editor de Visual Basic puede afectar significativamente al rendimiento de la función definida por el usuario de VBA, consulte la sección 'Funciones de VBA definidas por el usuario más rápidas' en Rendimiento de Excel: Sugerencias para salvar los obstáculos de rendimiento.For more information about how the Visual Basic Editor can significantly affect VBA user-defined function performance, see the 'Faster VBA user-defined functions' section in Excel performance: Tips for optimizing performance obstructions.
Para medir el tiempo de cálculo, debe llamar al método de cálculo adecuado.To measure calculation time, you must call the appropriate calculation method.Estas subrutinas le muestran el tiempo de cálculo para un rango, el tiempo de cálculo de una hoja o de todos los libros abiertos, o el tiempo de cálculo completo para todos los libros abiertos.These subroutines give you calculation time for a range, recalculation time for a sheet or all open workbooks, or full calculation time for all open workbooks.
Copie todas estas subrutinas y funciones en un módulo de VBA estándar.Copy all these subroutines and functions into a standard VBA module.Presione ALT+F11 para abrir el editor de VBA.To open the VBA editor, press Alt+F11.En el menú Insertar, seleccione Módulo y, a continuación, copie el código en el módulo.On the Insert menu, select Module, and then copy the code into the module.
Para ejecutar las subrutinas en Excel, presione ALT+F8.To run the subroutines in Excel, press Alt+F8.Seleccione la subrutina que desee y, a continuación, haga clic en Ejecutar.Select the subroutine you want, and then click Run.
Figura 5. La ventana de macros de Excel que muestra los temporizadores de cálculoFigure 5. The Excel Macro window showing the calculation timers
Buscar y priorizar obstáculos de cálculoFinding and prioritizing calculation obstructions
La mayoría de libros con cálculos lentos tienen solo unas pocas áreas problemáticas u obstáculos que consumen la mayoría del tiempo de cálculo.Most slow-calculating workbooks have only a few problem areas or obstructions that consume most of the calculation time.Si no sabe ya dónde se encuentran, use el método de obtención de detalles descrito en esta sección para encontrarlos.If you do not already know where they are, use the drill-down approach outlined in this section to find them.Si sabe dónde se encuentran, debe medir el tiempo de cálculo que usa cada obstrucción para poder establecer prioridades en el trabajo para eliminarlos.If you do know where they are, you must measure the calculation time that is used by each obstruction so that you can prioritize your work to remove them.
Enfoque de obtención de detalles para encontrar obstruccionesDrill-down approach to finding obstructions
El enfoque de obtención de detalles empieza por medir el tiempo de cálculo del libro, el cálculo de cada hoja de cálculo y los bloques de fórmulas en hojas de cálculo lentas.The drill-down approach starts by timing the calculation of the workbook, the calculation of each worksheet, and the blocks of formulas on slow-calculating sheets.Realice cada paso en orden y anote los tiempos de cálculo.Do each step in order and note the calculation times.
Para buscar obstrucciones con el método de obtención de detallesTo find obstructions using the drill-down approach
Asegúrese de que tiene un único libro abierto y de que no se ejecutan otras tareas.Ensure that you have only one workbook open and no other tasks are running.
Establezca el cálculo en manual.Set calculation to manual.
Realice una copia de seguridad del libro.Make a backup copy of the workbook.
Abra el libro que contiene las macros de temporizador de cálculo o agréguelas al libro.Open the workbook that contains the Calculation Timers macros, or add them to the workbook.
Compruebe el rango utilizado presionando Ctrl+End en cada hoja por separado.Check the used range by pressing Ctrl+End on each worksheet in turn.
Esto muestra dónde está la última celda utilizada.This shows where the last used cell is.Si se trata de una posición más allá de la que esperaba, considere la posibilidad de eliminar las columnas y filas sobrantes y de guardar el libro. If this is beyond where you expect it to be, consider deleting the excess columns and rows and saving the workbook.Para obtener más información, consulte la sección 'Reducir el rango utilizado' en Rendimiento de Excel: Sugerencias para salvar los obstáculos de rendimiento.For more information, see the 'Minimizing the used range' section in Excel performance: Tips for optimizing performance obstructions.
Ejecute la macro FullCalcTimer.Run the FullCalcTimer macro.
El tiempo para calcular todas las fórmulas del libro suele ser el peor de los casos.The time to calculate all the formulas in the workbook is usually the worst-case time.
Ejecute la macro RecalcTimer.Run the RecalcTimer macro.
Normalmente, una actualización después de un cálculo completo le muestra el mejor tiempo posible.A recalculation immediately after a full calculation usually gives you the best-case time.
Calcule la volatilidad del libro como la relación de tiempo de actualización con el tiempo de cálculo completo.Calculate workbook volatility as the ratio of recalculation time to full calculation time.
Esto mide el grado en que las fórmulas volátiles y la evaluación de la cadena de cálculo son obstrucciones.This measures the extent to which volatile formulas and the evaluation of the calculation chain are obstructions.
Active cada hoja y ejecute la macro SheetTimer por turnos.Activate each sheet and run the SheetTimer macro in turn.
Dado que acaba de volver a calcular el libro, esto le da el tiempo de actualización de cada hoja de cálculo. Because you just recalculated the workbook, this gives you the recalculate time for each worksheet.Esto debería permitirle determinar cuáles son las hojas de cálculo con problemas.This should enable you to determine which ones are the problem worksheets.
Ejecute la macro RangeTimer en bloques de fórmulas seleccionados.Run the RangeTimer macro on selected blocks of formulas.
Para cada hoja de cálculo con problemas, divida las columnas o las filas en un pequeño número de bloques.For each problem worksheet, divide the columns or rows into a small number of blocks.
Seleccione cada bloque uno a uno y ejecute la macro RangeTimer en el bloque.Select each block in turn, and then run the RangeTimer macro on the block.
Si es necesario, para profundizar, subdivida cada bloque en un número menor de bloques.If necessary, drill down further by subdividing each block into a smaller number of blocks.
Establezca la prioridad de los obstáculos.Prioritize the obstructions.
Acelerar cálculos y reducir obstáculosSpeeding up calculations and reducing obstructions
No es el número de fórmulas o el tamaño de un libro lo que aumenta el tiempo de cálculo.It is not the number of formulas or the size of a workbook that consumes the calculation time.Es el número de operaciones de cálculo y referencias de celda, junto con la eficacia de las funciones que se usan.It is the number of cell references and calculation operations, and the efficiency of the functions being used.
Puesto que la mayoría de las hojas de cálculo se crean mediante la copia de fórmulas que contienen una combinación de referencias absolutas y relativas, normalmente contienen un gran número de fórmulas que contienen cálculos y referencias repetidos o duplicados.Because most worksheets are constructed by copying formulas that contain a mixture of absolute and relative references, they usually contain a large number of formulas that contain repeated or duplicated calculations and references.
Evite megafórmulas complejas y fórmulas de matriz.Avoid complex mega-formulas and array formulas.En general, es mejor tener más filas y columnas y menos cálculos complejos.In general, it is better to have more rows and columns and fewer complex calculations.Esto proporciona a la actualización inteligente y al cálculo multiproceso de Excel una mejor oportunidad para optimizar los cálculos. This gives both the smart recalculation and the multithreaded calculation in Excel a better opportunity to optimize the calculations.También es más fácil de comprender y depurar. It is also easier to understand and debug.Los siguientes son algunas reglas para ayudar a acelerar los cálculos del libro.The following are a few rules to help you speed up workbook calculations.
Primera regla: quitar cálculos innecesarios, duplicados y repetidosFirst rule: Remove duplicated, repeated, and unnecessary calculations
Busque cálculos duplicados, repetidos e innecesarios y calcule aproximadamente el número de referencias de celda y cálculos que necesita Excel para calcular el resultado de esta obstrucción. Look for duplicated, repeated, and unnecessary calculations, and figure out approximately how many cell references and calculations are required for Excel to calculate the result for this obstruction.Piense en cómo puede obtener el mismo resultado con menos referencias y cálculos.Think how you might obtain the same result with fewer references and calculations.
Normalmente, esto implica uno o varios de los pasos siguientes:Usually this involves one or more of the following steps:
Reducir el número de referencias en cada fórmula.Reduce the number of references in each formula.
Mueva los cálculos repetidos a una o más celdas auxiliares y, a continuación, haga referencia a las celdas auxiliares de las fórmulas originales.Move the repeated calculations to one or more helper cells, and then reference the helper cells from the original formulas.
Use filas y columnas adicionales para calcular y almacenar los resultados intermedios una vez, de modo que pueda volver a utilizarlos en otras fórmulas.Use additional rows and columns to calculate and store intermediate results once so that you can reuse them in other formulas.
Segunda regla: usar la función más eficiente posibleSecond rule: Use the most efficient function possible
Cuando encuentre un obstáculo que implique una función o fórmulas de matriz, determine si hay una forma más eficaz de obtener el mismo resultado.When you find an obstruction that involves a function or array formulas, determine whether there is a more efficient way to achieve the same result.Por ejemplo:For example:
Las búsquedas en datos ordenados pueden ser decenas o centenares de veces más eficientes que las búsquedas en datos no ordenados.Lookups on sorted data can be tens or hundreds of times more efficient than lookups on unsorted data.
Las funciones definidas por el usuario de VBA son normalmente más lentas que las funciones integradas de Excel (aunque las funciones de VBA escritas cuidadosamente pueden ser rápidas).VBA user-defined functions are usually slower than the built-in functions in Excel (although carefully written VBA functions can be fast).
Minimice el número de celdas usadas en funciones como SUM y sumar.Si.Minimize the number of used cells in functions like SUM and SUMIF.El tiempo de cálculo es proporcional al número de celdas usadas (se ignoran las celdas sin usar).Calculation time is proportional to the number of used cells (unused cells are ignored).
Considere la posibilidad de reemplazar las fórmulas de matriz lentas por funciones definidas por el usuario.Consider replacing slow array formulas with user-defined functions.
Tercera regla: hacer un buen uso de la actualización inteligente y el cálculo multiprocesoThird rule: Make good use of smart recalculation and multithreaded calculation
Cuanto mejor uso haga de la actualización inteligente y el cálculo multiproceso en Excel, menor es el procesamiento que debe realizarse cada vez que Excel actualiza, de este modo:The better use you make of smart recalculation and multithreaded calculation in Excel, the less processing has to be done every time that Excel recalculates, so:
Evite funciones volátiles como INDIRECTO y DESREF donde pueda, a menos que sean significativamente más eficientes que las alternativas.Avoid volatile functions such as INDIRECT and OFFSET where you can, unless they are significantly more efficient than the alternatives.(El uso bien diseñado de DESREF suele ser rápido).(Well-designed use of OFFSET is often fast.)
Minimice el tamaño de los rangos que usa en fórmulas y funciones de matriz.Minimize the size of the ranges that you are using in array formulas and functions.
Divida las fórmulas de matriz y megafórmulas en filas y columnas auxiliares independientes.Break array formulas and mega-formulas out into separate helper columns and rows.
Evite las funciones de subproceso único:Avoid single-threaded functions:
- PHONETICPHONETIC
- CELL cuando se usa el argumento 'format' o 'address'CELL when either the 'format' or 'address' argument is used
- INDIRECTINDIRECT
- GETPIVOTDATAGETPIVOTDATA
- CUBEMEMBERCUBEMEMBER
- CUBEVALUECUBEVALUE
- CUBEMEMBERPROPERTYCUBEMEMBERPROPERTY
- CUBESETCUBESET
- CUBERANKEDMEMBERCUBERANKEDMEMBER
- CUBEKPIMEMBERCUBEKPIMEMBER
- CUBESETCOUNTCUBESETCOUNT
- ADDRESS donde se proporciona el quinto parámetro (sheet_name)ADDRESS where the fifth parameter (the sheet_name) is given
- Cualquier función de base de datos (BDSUMA, BDPROMEDIO, etc.) que haga referencia a una tabla dinámicaAny database function (DSUM, DAVERAGE, and so on) that refers to a pivot table
- ERROR.TYPEERROR.TYPE
- HYPERLINKHYPERLINK
- Funciones definidas por el usuario de complementos de VBA y COMVBA and COM add-in user-defined functions
Evite el uso iterativo de tablas de datos y las referencias circulares: estos dos cálculos siempre se calculan en un único subproceso.Avoid iterative use of data tables and circular references: both of these always calculate single-threaded.
Cuarta regla: mida el tiempo y pruebe cada cambioFourth rule: Time and test each change
Algunos de los cambios que realiza pueden sorprenderle, ya sea mostrando una respuesta que no esperaba o calculando más lentamente de lo esperado.Some of the changes that you make might surprise you, either by not giving the answer that you thought they would, or by calculating more slowly than you expected.Por lo tanto, debería medir tiempo y probar cada cambio, como sigue:Therefore, you should time and test each change, as follows:
Mida el tiempo de la fórmula que quiere cambiar mediante la macro RangeTimer.Time the formula that you want to change by using the RangeTimer macro.
Realice el cambio.Make the change.
Mida el tiempo de la fórmula cambiada con la macro RangeTimer.Time the changed formula by using the RangeTimer macro.
Compruebe que la fórmula modificada todavía proporciona la respuesta correcta.Check that the changed formula still gives the correct answer.
Ejemplos de reglasRule examples
Las secciones siguientes proporcionan ejemplos de cómo usar las reglas para acelerar el cálculo.The following sections provide examples of how to use the rules to speed up calculation.
Sumas de período hasta la fechaPeriod-to-date sums
Por ejemplo, debe calcular las sumas de 'período hasta la fecha' de una columna que contiene 2 000 números.For example, you need to calculate the period-to-date sums of a column that contains 2,000 numbers.Supongamos que la columna A contiene los números y que la columna B y la columna C deben contener los totales de 'período hasta la fecha'.Assume that column A contains the numbers, and that column B and column C should contain the period-to-date totals.
Podría escribir la fórmula utilizando SUMA, que es una función eficaz.You could write the formula using SUM, which is an efficient function.
Figura 6. Ejemplo de fórmulas de suma de 'período hasta la fecha'Figure 6. Example of period-to-date SUM formulas
Copie la fórmula hasta B2000.Copy the formula down to B2000.
¿Cuántas referencias de celda agrega SUMA en total?How many cell references are added up by SUM in total?B1 hace referencia a una celda y B2000 hace referencia a 2 000 celdas.B1 refers to one cell, and B2000 refers to 2,000 cells.El promedio es 1 000 referencias por celda, por lo que el número total de referencias es 2 millones.The average is 1,000 references per cell, so the total number of references is 2 million.Al seleccionar las 2 000 fórmulas y utilizar la macro RangeTimer se muestra que las 2 000 fórmulas en la columna B se calculan en 80 milisegundos.Selecting the 2,000 formulas and using the RangeTimer macro shows you that the 2,000 formulas in column B calculate in 80 milliseconds.La mayoría de estos cálculos están duplicados muchas veces: SUMA agrega A1 a A2 en cada fórmula de B2:B2000.Most of these calculations are duplicated many times: SUM adds A1 to A2 in each formula from B2:B2000.
Puede eliminar esta duplicación si escribe las fórmulas de la siguiente manera.You can eliminate this duplication if you write the formulas as follows.
Copie esta fórmula hacia abajo hasta C2000.Copy this formula down to C2000.
¿Ahora cuántas referencias de celda se agregan en total?Now how many cell references are added up in total?Cada fórmula, excepto la primera fórmula, utiliza dos referencias de celda.Each formula, except the first formula, uses two cell references.Por lo tanto, el total es 1999 * 2 + 1 = 3 999.Therefore, the total is 1999*2+1=3999.Este es un factor de 500 menos referencias de celda.This is a factor of 500 fewer cell references.
RangeTimer indica que las 2 000 fórmulas de la columna C se calculan en 3,7 milisegundos con respecto a los 80 milisegundos de la columna B. Este cambio tiene un factor de mejora del rendimiento de solo 80/3,7=22 en lugar de 500 porque hay una pequeña sobrecarga por fórmula.RangeTimer indicates that the 2,000 formulas in column C calculate in 3.7 milliseconds compared to the 80 milliseconds for column B. This change has a performance improvement factor of only 80/3.7=22 instead of 500 because there is a small overhead per formula.
Control de erroresError handling
Si tiene una fórmula de cálculo intensivo en la que desea que el resultado se muestre como cero si se produce un error (esto ocurre con frecuencia con las búsquedas de coincidencia exacta), puede escribir esto de varias formas.If you have a calculation-intensive formula where you want the result to be shown as zero if there is an error (this frequently occurs with exact match lookups), you can write this in several ways.
Se puede escribir como una única fórmula, que es lento:You can write it as a single formula, which is slow:
B1=IF(ISERROR(time expensive formula),0,time expensive formula)Puede escribirlo como dos fórmulas, que es rápido:You can write it as two formulas, which is fast:Mcculloch mac 3200 chainsaw manual.
A1=time expensive formulaB1=IF(ISERROR(A1),0,A1)También puede usar la función SI.ERROR, que está diseñada para ser rápida y sencilla y es una única fórmula:Or you can use the IFERROR function, which is designed to be fast and simple, and is a single formula:
B1=IFERROR(time expensive formula,0)
Recuento único dinámicoDynamic count unique
Figura 7. Lista de ejemplo de datos para recuento únicoFigure 7. Example list of data for count unique
Si tiene una lista de 11 000 filas de datos en la columna A, que cambia con frecuencia, y necesita una fórmula que calcule dinámicamente el número de elementos únicos de la lista y omita los espacios en blanco, a continuación se muestran varias soluciones posibles.If you have a list of 11,000 rows of data in column A, which frequently changes, and you need a formula that dynamically calculates the number of unique items in the list, ignoring blanks, following are several possible solutions.
Fórmulas de matriz (use Ctrl+Mayús+Entrar); RangeTimer indica que esto le llevará 13,8 segundos.Array formulas (use Ctrl+Shift+Enter); RangeTimer indicates that this takes 13.8 seconds.
SUMAPRODUCTO normalmente calcula más rápido que una fórmula de matriz equivalente.SUMPRODUCT usually calculates faster than an equivalent array formula.Esta fórmula tarda 10,0 segundos y proporciona un factor de mejora de 13,8/10,0 = 1,38, que es mejor, pero no es lo suficientemente bueno.This formula takes 10.0 seconds, and gives an improvement factor of 13.8/10.0=1.38, which is better, but not good enough.
Funciones definidas por el usuario.User-defined functions.En el ejemplo de código siguiente se muestra una función definida por el usuario de VBA que usa el hecho de que el índice de una colección debe ser único.The following code example shows a VBA user-defined function that uses the fact that the index to a collection must be unique.Para obtener una explicación de algunas técnicas que usan, vea la sección acerca de las funciones definidas por el usuario en la sección 'Usar funciones de forma eficaz' en Rendimiento de Excel: Sugerencias para salvar los obstáculos de rendimiento.For an explanation of some techniques that are used, see the section about user-defined functions in the 'Using functions efficiently' section in Excel performance: Tips for optimizing performance obstructions.Esta fórmula,
=COUNTU(A2:A11000), tarda solo 0,061 segundos.This formula,=COUNTU(A2:A11000), takes only 0.061 seconds.Esto le proporciona un factor de mejora de 13,8/0,061=226.This gives an improvement factor of 13.8/0.061=226.Agregar una columna de fórmulas.Adding a column of formulas.Si observa el ejemplo anterior de datos, puede ver que está ordenado (Excel tarda 0,5 segundos en ordenar las 11 000 filas).If you look at the previous sample of the data, you can see that it is sorted (Excel takes 0.5 seconds to sort the 11,000 rows).Puede aprovechar esto agregando una columna de fórmulas que compruebe si los datos de esta fila son los mismos que los datos de la fila anterior.You can exploit this by adding a column of formulas that checks if the data in this row is the same as the data in the previous row.Si son diferentes, la fórmula devuelve 1.If it is different, the formula returns 1.De lo contrario, devuelve 0.Otherwise, it returns 0.
Agregue esta fórmula a la celda B2.Add this formula to cell B2.
Copie la fórmula y, a continuación, agregue una fórmula para agregar la columna B.Copy the formula, and then add a formula to add up column B.
Un cálculo completo de todas estas fórmulas tardará 0,027 segundos.A full calculation of all these formulas takes 0.027 seconds.Esto le proporciona un factor de mejora de 13,8/0,027=511.This gives an improvement factor of 13.8/0.027=511.
ConclusiónConclusion
Excel le permite administrar de manera eficaz hojas de cálculo mucho más grandes y ofrece mejoras importantes en la velocidad de cálculo en comparación con las versiones anteriores.Excel enables you to effectively manage much larger worksheets, and it provides significant improvements in calculation speed compared with early versions.Al crear hojas de cálculo de gran tamaño, es fácil crearlas de forma que provoque lentitud en los cálculos.When you create large worksheets, it is easy to build them in a way that causes them to calculate slowly.Las hojas de cálculo lentas aumentan los errores porque a los usuarios les resulta difícil mantener la concentración mientras se produce el cálculo.Slow-calculating worksheets increase errors because users find it difficult to maintain concentration while calculation is occurring.
Al usar un conjunto de técnicas sencillo, puede acelerar la mayoría de las hojas con cálculo lento en un factor de 10 o 100.By using a straightforward set of techniques, you can speed up most slow-calculating worksheets by a factor of 10 or 100.También puede aplicar estas técnicas al diseñar y crear hojas de cálculo para asegurarse de que calculan rápidamente.You can also apply these techniques as you design and create worksheets to ensure that they calculate quickly.
Vea tambiénSee also
Soporte técnico y comentariosSupport and feedback
Calculo Manual Excel Machine
¿Tiene preguntas o comentarios sobre VBA para Office o esta documentación?Have questions or feedback about Office VBA or this documentation?Vea Soporte técnico y comentarios sobre VBA para Office para obtener ayuda sobre las formas en las que puede recibir soporte técnico y enviar comentarios.Please see Office VBA support and feedback for guidance about the ways you can receive support and provide feedback.
If you have large workbooks with a lot of formulas on the worksheets, recalculating the workbooks can take a long time. By default, Excel automatically recalculates all open workbooks as you change values in the worksheets. However, you can choose to recalculate only the current worksheet manually.
Notice I said worksheet, not workbook. There is no direct way in Excel to manually recalculate only the current workbook, but you can manually recalculate the current worksheet within a workbook.
To begin, click the “File” tab.
On the backstage screen, click “Options” in the list of items on the left.
The Excel Options dialog box displays. Click “Formulas” in the list of items on the left.
In the Calculation options section, click the “Manual” radio button to turn on the ability to manually calculate each worksheet. When you select “Manual”, the “Recalculate workbook before saving” check box is automatically checked. If you save your worksheet often and would rather not wait for it to recalculate every time you do, select the “Recalculate workbook before saving” check box so there is NO check mark in the box to disable the option.
You’ll also notice the “Automatic except for data tables” option. Data tables are defined by Microsoft as:
“. . . a range of cells that shows how changing one or two variables in your formulas will affect the results of those formulas. Data tables provide a shortcut for calculating multiple results in one operation and a way to view and compare the results of all the different variations together on your worksheet.”
Data tables are recalculated every time a worksheet is recalculated, even if they have not changed. If you’re using a lot of data tables, and you still want to automatically recalculate your workbooks, you can select the “Automatic except for data tables” option, and everything except for your data tables will be recalculated, saving you some time during recalculation.
If you don’t mind the “Recalculate workbook before saving” option being enabled when you turn on Manual calculation, there is a quicker way of choosing to manually recalculate your worksheets. First, click the “Formulas” tab.
Then, in the Calculation section of the Formulas tab, click the “Calculation Options” button and select “Manual” from the drop-down menu.
Once you’ve turned on manual calculation, you can click “Calculate Sheet” in the Calculation section of the Formulas tab, or press Shift+F9, to manually recalculate the active worksheet. If you want to recalculate everything on all worksheets in all open workbooks that has changed since the last calculation, press F9 (only if you have turned off Automatic calculation). To recalculate all formulas in all open workbooks, regardless of whether they have changed since the last recalculation, press Ctrl+Alt+F9. To check formulas that depend on other cells first and then recalculate all formulas in all open workbooks, regardless of whether they have changed since the last recalculation, press Ctrl+Shift+Alt+F9.
READ NEXT- › How to Make Your Family Love Your Smarthome
- › How to Enable Google Chrome’s New Extensions Menu
- › How to Stop Spammers From Attacking Your Google Calendar
- › How to Power Off Your Samsung Galaxy Note 10 or 10 Plus
- › How to Switch from a Windows PC to a Mac